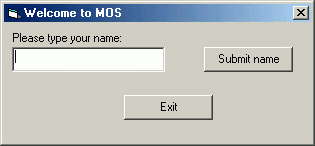
This program asks the user to type their name. When they click on "Submit", a message box will pop up that welcomes them. When they click on "Exit", the program quits.
Try out the program: welcome.exe (Click on the link and select "Run".)
Here's a description of the internals of this program.
Controls:
The main Form has all default properties, except that it was resized, the name is set to FormWelcome, the Caption was changed to "Welcome to MOS" and MaxButton and MinButton are both set to False. In the Form Layout window, the form was moved to the center of the screen.
There is a Label which has default properties, except that it has been repositioned, the name is set to lblNamePrompt, AutoSize is set to True, and Caption is set to "Please type your name:"
There is a TextBox which has all default properties, except that it has been repositioned and resized, the Name is set to txtUserName, Text has been set to be empty, and ToolTipText has been set to "Enter your name here".
There is a CommandBox which has all default properties, except that it has been repositioned and resized, the Name has been set to cmdSubmitName, the Caption has been set to "Submit name", and the ToolTipText has been set to "Click here to submit name".
There is a CommandBox which has all default properties, except that it has been repositioned and resized, the Name has been set to cmdExit, the Caption has been set to "Exit", and the ToolTipText has been set to "Click here to end program".
Here's the code:
' Exit the program if the Exit button is clicked
Private Sub cmdExit_Click()
End
End Sub
' When the Submit button is clicked, put up a message box that welcomes them
Private Sub cmdSubmitName_Click()
MsgBox ("Hello, " & txtUserName.Text & ". Welcome to MOS!")
End Sub
Notice that to find out the user's name, we just used the Text property from the txtUserName control. When you're writing code, to get access to a property of a control, you type the Name of the control, followed by .propertyname. You can access any property from any control this way. Most properties from most controls can also be altered in code as well, as we'll see in the next example. The properties in our controls are a type of variable. A variable is a named location in main memory that allows us to store information. When we create a control, we automatically get variables to store their properties. Later we'll see how to create other variables to store information that is not attached to controls.
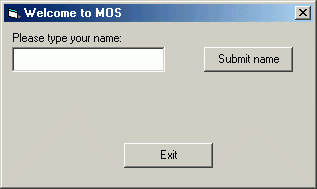
Try out the second program: welcome2.exe (Click on the link and select "Open".) This program for the most part has all the same controls as the previous program, except it has an additional label. This label has the default properties, except that it has been resized and repositioned, its Name is lblOutputMessage, and its caption is set to empty. Because we don't want the message to show up until the user has submitted their name, we set the Visible property to False. When the Submit button is clicked, the caption in the lblOutputMessage is set to the what we want the message to be, and the Visible property is turned on.
Here's a screen shot of the program as it is opened:
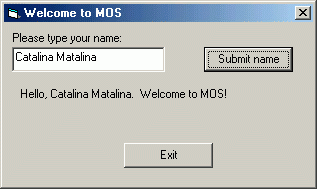
Here's a screen shot of the program after the name has been submitted:
Here's the part of the code that was changed from the previous example:
' When the Submit button is clicked, display a message. It is displayed
' in a label by setting the Text for the label to the welcome message,
' then making the label visible.
' The message says hello, then the user's name (taken from the txtUserName
' TextBox), then Welcome to MOS!
Private Sub cmdSubmitName_Click()
lblOutputMessage.Caption = "Hello, " & txtUserName.Text & ". Welcome to MOS!"
lblOutputMessage.Visible = True
End Sub
The first line of this code is accessing the Text property of the label
called lblOutputMessage. But instead of just using the value stored
there, this line of code is actually changing the value of the Text property.
The "=" is
called an assignment. Any time you see an "=" in BASIC code, it means to
take the value on the right hand side, and actually store it
in the variable on the left-hand side. This changes the value stored
in the variable while the program is running. The second line is another
example of an assignment statement. Assignment statements are extremely
important in programming, and we will use them often.